Towards an Error-free Deep Occupancy Detector for Smart Camera Parking System
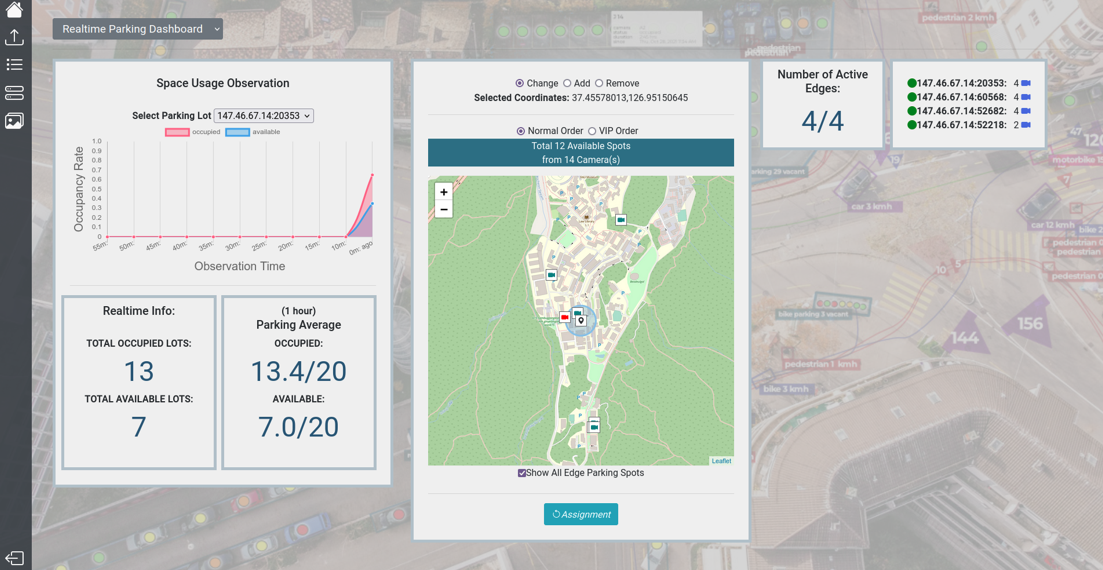
CVCIE (ECCV Workshop)Although the smart camera parking system concept has existed for decades, a few approaches have fully addressed the system's scalability and reliability. As the cornerstone of a smart parking system is the ability to detect occupancy, traditional methods use the classification backbone to predict spots from a manual labeled grid. This is time-consuming and loses the system's scalability. Additionally, most of the approaches use deep learning models, making them not error-free and not reliable at scale. Thus, we propose an end-to-end smart camera parking system where we provide an autonomous detecting occupancy by an object detector called OcpDet. Our detector also provides meaningful information from contrastive modules: training and spatial knowledge, which avert false detections during inference. We benchmark OcpDet on the existing PKLot dataset and reach competitive results compared to traditional classification solutions. We also introduce an additional SNU-SPS dataset, in which we estimate the system performance from various views and conduct system evaluation in parking assignment tasks. The result from our dataset shows that our system is promising for real-world applications.
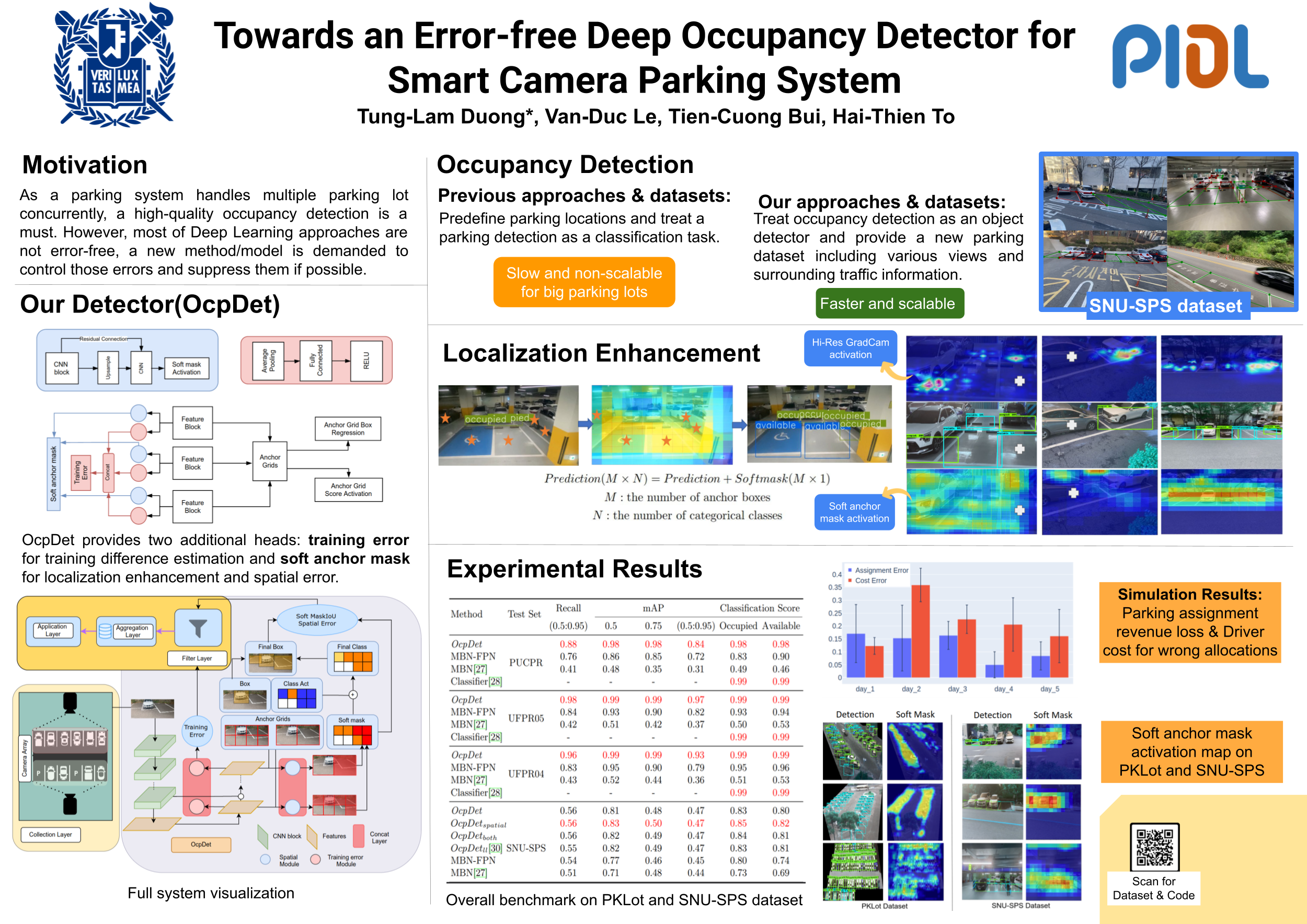
SNU-SPS Dataset
 Overview of SNU-SPS dataset
Overview of SNU-SPS dataset
- Image Acquisition:
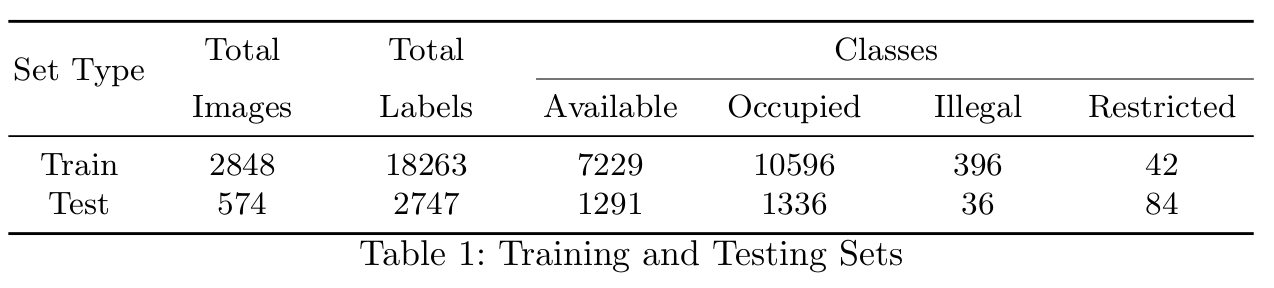
- All images are captured with a full-HD resolution. For the training set, it is captured randomly for one month in 15 parking lots. Meanwhile, the test set is captured consecutively in 6 parking lots from 3-6pm through 5 working days. It should be noted that none of the 6 parking lots are in the training set. Moreover, test samples contains various weather conditions (sun/rain/cloudy) and has corresponding surrounding traffic measurements from the open government website.
- Image Labeling:
- For each parking sector, images were labeled as available/ occupied/ illegal/ restricted of each parking space. Each annotation is covered by four keypoints that specify for the localization of a parking lot. We formulate the wrapping bounding boxes for the detector from these key points. Especially, we provide optional image masks for the test set to filter out overlapping areas and non-important localization among capture among parking lots. The intention is to maintain the system’s constraints and preserve a better parking assignment benchmark.
 Details of SNU-SPS dataset
Details of SNU-SPS dataset
Fault Tolerance Parking System
The overall architecture is designed for a full webservice integration, which is my thesis and going to be released in this November. Through the overall architecture, we demonstrated the intergration of spatial module and training error module in filtering wrong detections and storing for annotations. Images/captures after those grading will be noticed in the system so that its result won't be counted in the aggregation process. In the following part, the main ingredient of training and creating OcpDet will be introduced.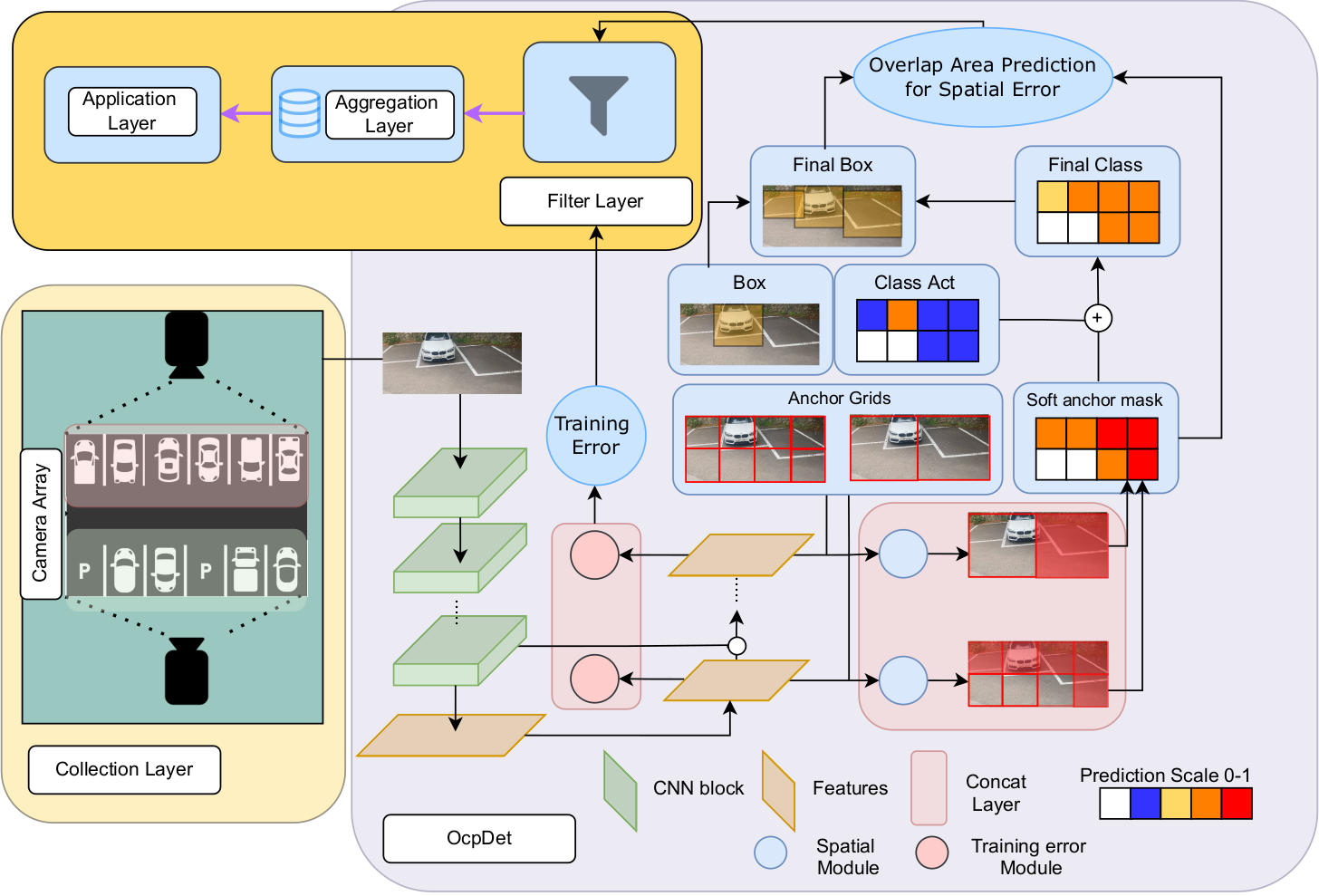 Overall Architecture
Overall Architecture
OcpDet Detector
As we aim to capture both high level features and low level features of the input image throughout the model interpretation, which combine the information of the parking borders/lines and the object inside those. Thus, Our OcpDet inherited the structure of Retina detector for this mechanism. However, we conduct additional modification on this architecture. First of all, instead of regressing only the center and the width of the bounding boxes, we integrate 4 others keypoints as new outcomes for the model (which is provided from our dataset).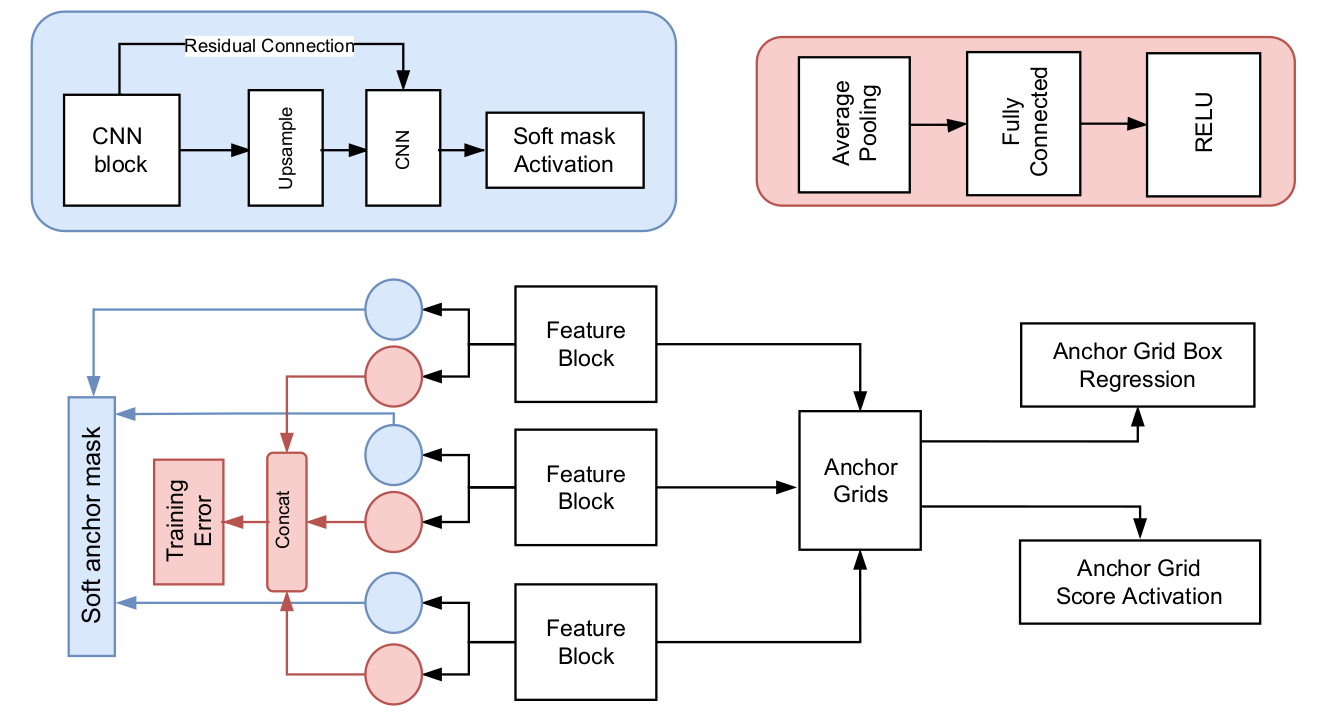 Modules Architecture: each block is attached to the FPN feature level for its training and prediction
Modules Architecture: each block is attached to the FPN feature level for its training and prediction
- Training Error Estimator:
- For training error, we integrate the Learning Loss approach to predict the error of the prediction/predict the loss that the image can cause. Based on this loss, we can replicate how much the loss will be for the output if we labeled and compute for an input. However, to make the Learning Loss behave better with the dataset statistic, we sample the predicted Learning Loss over the dataset as its mean and variance and compare inferenced samples by a distribution distance to these statistics.
-
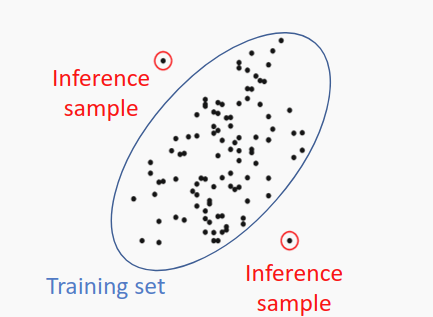

Error training samples behavior (on the left) & Error determination/Spatial error (on the right) - Spatial Estimator:
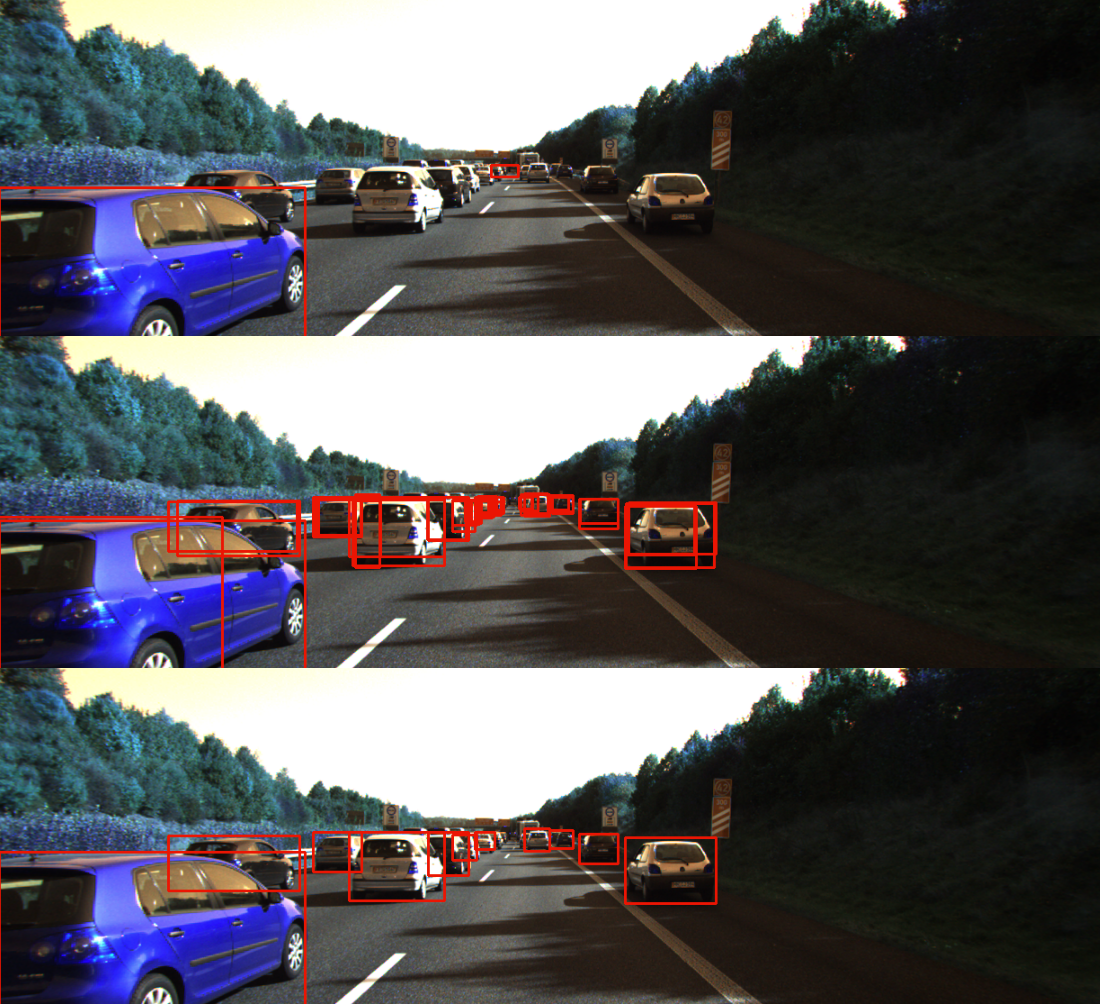
- As most of our nowadays detection focus on grid and anchor boxes, the prediction is filtered by a threshold value and background value. This can cause a situation where a correct activation anchor box has a score below this threshold, or a slight below the background confidence. Therefore, we provide an easy-integrated method by predicting the active anchor boxes in the scene by attaching another CNN module beside the Training Error Estimator and predict a mask of active anchors. This can be done reliably as the parking spots are equally patched in the scenes and can be well covered by different level of anchors. From this mask, we can suppress wrong detections by decreasing their confidence and enhance high-confidence anchors.
- For formulation, each block of the spatial module will predict a 2D mask corresponding to the anchors of the same branch prediction. This mask then will be reduce by a confidence threshold before combining with the confidence prediction branch for suppression and enhancement. The blue color showing in the result picture below meaning those anchor got suppressed (the confidence got minus), while the yellow is enhanced (the confidence got increased). Noted that, this is done on all classes except the background
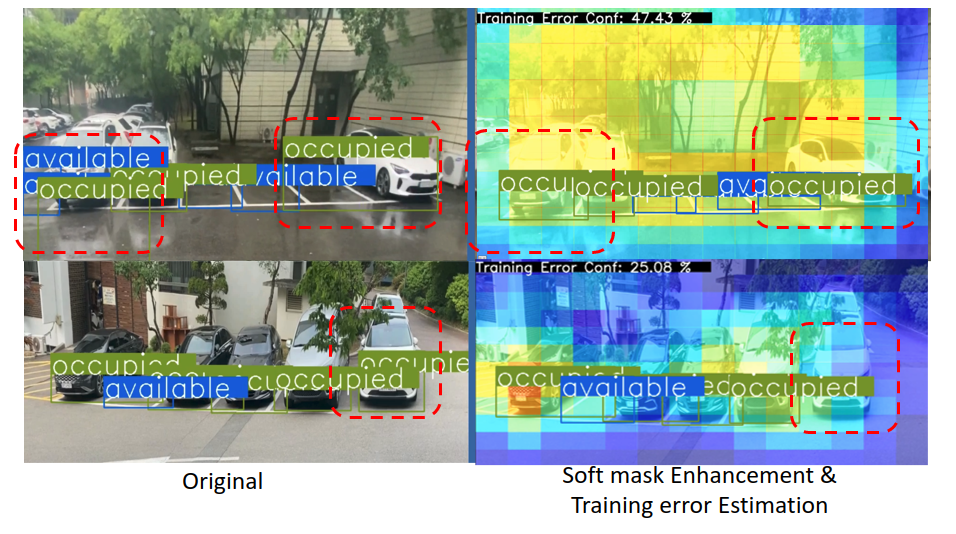 The results of these two modules
The results of these two modules